How to configure user resource limits and restrictions in Linux

Before discussing this, I would briefly like to touch on PAM (Pluggable Authentication Module) in Linux. PAM helps us to authenticate. Meanwhile, authentication is used by programs that provide users access to a system to be able to determine their identities. In Linux, especially centos and RedHat, many programs undergo configuration to make authentication possible from a central spot. Discover how to configure user resource limits and restrictions in Linux.
You can find other guides in these links: Practical use of SELinux in production: How to locate directory file context and restore it, how-to-create-a-static-pod-in-kubernetes-with-demos-that-can-help-you-become-a-better-kubernetes-administrator,how-to-create-and-deliver-a-report-on-system-utilization-on-a-linux-based-os/ and how-to-use-container-insights-to-get-the-full-benefits-of-azure-monitor-for-azure-kubernetes-workload/
User resource limits determine the amount of resources that can be used in a particular user session.
Steps in Configuring User Resource Limits
As the subject bothers on authentication and access, you should already have realized that we are being pointed to security. To configure access and limits for a user or groups of users, we should look at the configuration file in /etc/security.
Setting User Resource Limits
On the command line, we changed from where we were into /etc/security, and we then listed all the content in that directory as shown above. The particular file that we want to work on is limits. conf. So the next thing to do is to use a text editor like vim or nano to go into the configuration file limits. conf and make any changes that we want.
The configuration file on its own holds much valuable information that can guide us through setting user resource limits. The format it follows is <domain> <type> <item> <value>
A domain can be a user or group. Let us assume that we have a group called @techdirectarchive and a user called @raphael (it is always a good practice to put a @in front of a domain element). The type can either be a hard or a soft limit, item can be the size of the core, or the size of nproc. The value is usually the restriction that you want to set. If, for example, you want a particular group called coders to have only 30 processes running, the value will be 30.
Hard limit means that the limit will be enforced.
A soft limit is the type of limit that is not enforced immediately and sends a warning to the user before continuing the following line of action.
In the screenshot above @students means for members of the group students. In addition, there is a hard limit that sets the number of processes to 20. Please see how to resolve Account restrictions are preventing this user from signing in: User Account Password has expired.
Demo
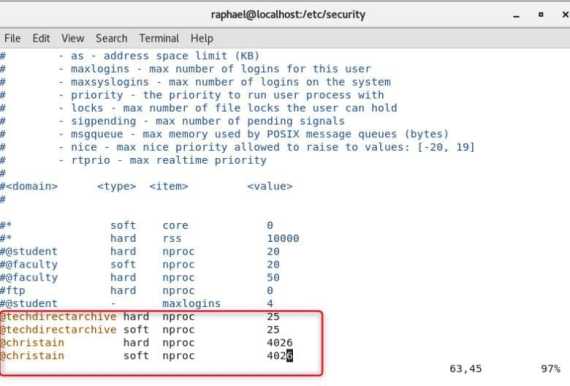
Assuming the @techdirectarchive team is using a server running low on resources. So that every memteam members a fair chance to use the server, we will be limiting the available resource. We will give configure @techdirectarchive group so that they can only start 25 processes . However, a user @christian will have privileged access so that he can start an unlimited number of methods. So guys, let’s head over to the console. Type the command shown in earlier steps and add it to the configuration file just shown in the screenshot below. The steps are below. With these steps, you can set user resource limits in Linux without hassle.
# cd /etc/security #ls # vim limits.conf
We just need to enter the insert mood if we are using vi editor. Then configure the file so that the group and user can have the type, item, and values as shown above
The default number of processes that a root privileged user can have is 4026
Summary
In conclusion, we can configure /etc/security‘s limit.conf with the specific domain, type, item, and value to reflect the desired requirement using a text editor. Overall, you’ve learned how to configure user resource limits in Linux.









Well, it’s possible but as we all know, the more resources you have on a system the better it is for you as a user. We can use the command ulimit – S to increase resources on a soft limit. S Indicate that the resource’s soft limit has been set. A soft limit can be raised up to the hard limit’s value. If you don’t add the -S or -H flag the system will take it that you applied the increase to both Hard and Soft limit, So it’s good to specify. For hard limits, only a user with admin privileges will be able to change resource limits.
Thank you Raphael for this piece, I did not know system resources could be managed until now.
How do I save the new configuration after modifying the limits?
Hi Uzodinmma, thank you for reading, the particular config file in this article is limits. conf, it is a read-only vim file and there are about 5 commands that you can use to save a read-only vim file. The one I use is this, you hit ESCAPE on your keyboard then: w ! sudo tee % it will still be in read mode. The next thing to do is to hit ESCAPE:q! and u will be returned to the terminal
Thank you for response. It is much helpful.
Just as most config file, only root has the right to modify it, right?