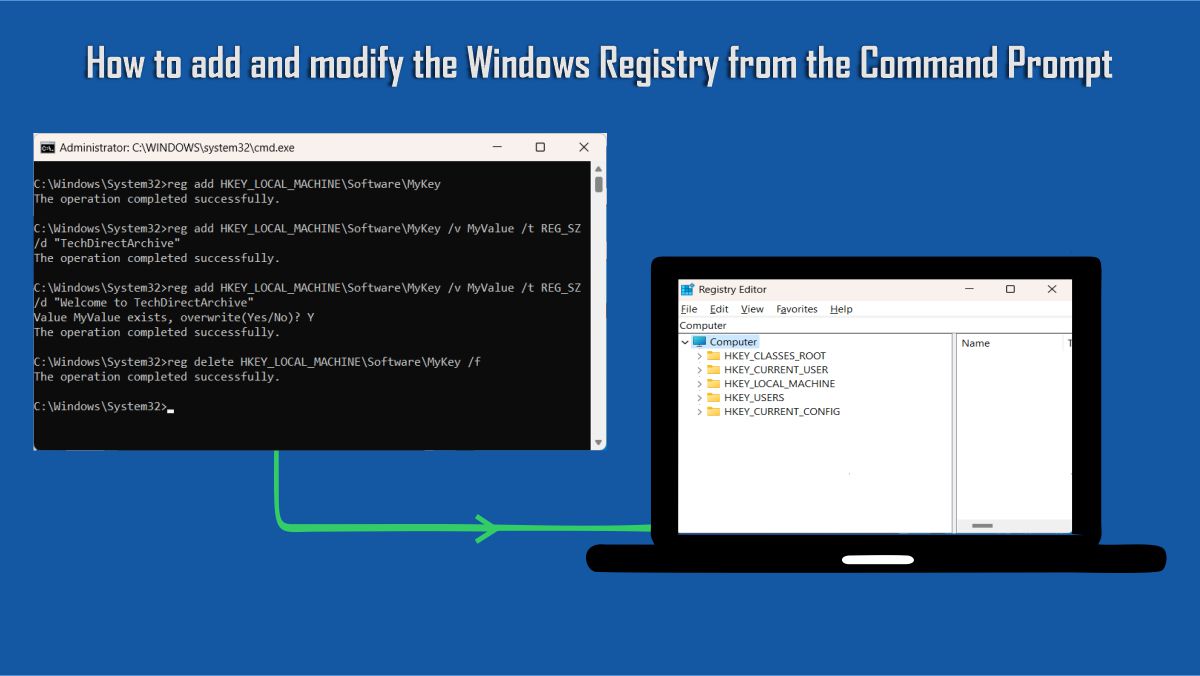
Setup a Domain Controller as Recommended by Microsoft

A Domain Controller (DC) responds to authentication requests. It has an hierarchical structure called domains. In this article, I will be discussing how to Setup a Domain Controller as Recommended by Microsoft in HyperV. Please see Pleasant User Group Permission and User Access, Domain Name System Protocol: Client Registration Issue, Domain Name System: How to create a DNS record, and how to fix “DNS Bad key 9017: The Cluster Name registration failed of one or more associated DNS names“.
When settings up a new Active Directory (AD), it is important to plan the DNS setup accordingly. DNS is the Domain Naming system used to translate names into network (IP) addresses.
Note: Discouraging the use of non-official internal domain names is crucial due to potential security and verification issues. In November 2015, SSL certificates for servers with non-public domain suffixes were withdrawn by Certificate Authorities (CAs) because public verification was not possible. Unofficial domain names lack routability and do not adhere to internet naming standards, making them unsuitable for widespread support.
Using a single DNS name space for internal and external services is also frowned at too. For example using a public registered domain name such as techdirectarchivedotcom can create a number of DNS, and security issues.
Active Directory Domain vs DNS name
The AD domain name differs from the DNS name but they are interconnected. The AD domain name primarily serves within AD operations, particularly for LDAP queries supporting AD functionality. In contrast, DNS functions as a network-level solution for resolving names to IP addresses. This distinction enables the utilization of an ‘internal,’ private AD domain name alongside a public, registered DNS.
This is why, the AD domain short name is referred as the NetBIOS Name (as in the AD logon name <DOMAIN>\username>).
Learn What happens when WDS and DNS are installed on the same Windows Server? DNS issues with WDS, and Video on how to Back Up and Restore Windows Registry.
Best Practice for DNS naming for internal domains and networks
Microsoft generally recommends using a subdomain of an existing domain for your Active Directory (AD) implementation. That is, a subdomain of a publicly registered top level domain. This is because AD is tightly integrated with DNS, and using a subdomain helps to isolate the AD namespace from the rest of your organisation’s DNS namespace. This isolation can be beneficial for management and security purposes.
Therefore, register a public DNS name such as techdirectarchivedotcom. Then create subdomains for internal use such as (tda.techdirectarchive.com).Plan your AD Domain Structure
Decide on the domain name you want to use for your AD. For example, if your organization’s public domain is exampledotcom, you might choose ad.exampledotcom for your Active Directory.
As discussed above, Microsoft generally recommends using a subdomain of an existing domain for your Active Directory (AD) implementation. This is because AD is tightly integrated with DNS, and using a subdomain helps to isolate the AD namespace from the rest of your organization’s DNS namespace. This isolation can be beneficial for management and security purposes.
Create a Virtual Machine for your Domain Controller
I will be using a VM created on HyperV. If you wish to follow my steps, please proceed and have a VM created on Hyper. Enter the VM name as shown below.

Enter the disk size. The can be extended later depending on your need. See how to fix unable to Extend Volume on Windows protected by BitLocker, and how to Increase Disk Size in Hyper-V.

Click Finish to complete the VM creation on HyperV.

Install Windows Server 2022 onto the HyperV VM
Now, you can start and connect to your VM.

Please start the VM.

Note: Ensure you enable Trusted Platform Module as shown below. This is disabled by default in HyperV VMs.

Click on Install to install the OS.

The OS is being installed.

Windows Server setup is complete. Enter your Admin password to access the OS.

Setup a Domain Controller as Recommended by Microsoft
As discussed extensively, the best practice remains to use a subdomain of a domain you own. For instance, if you own mydomaindotcom. Then you can consider using internal.mydomaindotcom for your internal network.
This approach ensures you align with standard practices and avoids potential issues with future TLDs or conflicts with mDNS or other services.
Here is how to Create local Backup Repository and Add HyperV to VBR Inventory, and video on how to Fix the Boot Failed UEFI SCSI Device on HyperV.
Install Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS)
After installing Windows Server, install the Active Directory Domain Services role. This can be done using the Server Manager

On the before you begin page, click Next

Select Role-based or feature-based installation and click next.

On the select destination server, click next.

Select “Active Directory Domain Services” under server roles and click next.

Click Add features at the prompt

We have selected to add the ADDS role

Click Next on the Select features page

This is just informational. Since this is an entirely new domain, I will be installing another DC very shortly. See

Kindly install the ADDS role.

The ADDS role is being installed.

Feel free to close the wizard at this time.

Learn from this video on how to Enable Find My Device on Windows 11, and also the video on how to increase Disk Size in Hyper-V.
Domain Controller Promotion
Promote the server to a domain controller using the Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard. This will involve specifying the domain name and providing Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM) password.

Specify the full domain name for the new forest as recommended by Microsoft. If you already have a DC. You can install additional domain controllers in the same domain.

The functional level establishes the characteristics and functionalities of Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) and dictates the available features within both the forest and the domain. It also influences the permissible server operating systems that can operate on Domain Controllers (DCs). Furthermore, it establishes the baseline ADDS functionality for all domains and all DCs within the domain.
The Domain Functional Level establishes the Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) functionality level for all domain controllers within the domain. You cannot set the Domain Functional Level below the Forest Functional Level, but you can set it higher.
If you have multiple domains, consider whether you need to configure the domain controller as a Global Catalog server. This is often recommended for better search performance in a multi-domain environment.
Set a password for Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM). This password is used to recover the domain controller if it fails

DNS Options
The authorization parent zone cannot be found, preventing the DNS server from creating the delegation. This issue arises due to the new installation, and currently, there is no dynamic Microsoft DNS server in place.
If you already have a DNS server, proceed by clicking next. If your organization hosts its DNS externally, you might need to create a DNS delegation for the subdomain to direct it to your internal DNS servers. This ensures that your internal DNS queries for the subdomain get resolved correctly.
Note: I will click next to install the DNS server on the domain controller. DNS is a crucial component of AD. If the DNS role is not already installed, it will be automatically installed during the promotion of the server to a domain controller.

NetBIOS, a protocol largely obsolete in contemporary settings, represents a technology predating Windows Server 2000. The default settings will be retained, and the next button will be clicked.
While the name can be altered at this stage, the pre-populated name is satisfactory for the current configuration.

Specify the locations for the AD DS database, log files, and SYSVOL

Review the options as shown below, and click next to continue.

The wizard performs a prerequisites check. If there are any issues, resolve them before proceeding

Prerequisite check passed. Click on Install

The server will automatically restart after the Active Directory installation is complete. See this guide if you wish to demote and remove a Domain Controller on Windows Servers.

Post-Installation Steps
I would recommend you implement best practices for securing your Active Directory environment. This includes enabling some Group Policy settings, creating organisational unit (OU) structure, and users account setup and group group creation and permissions assignment.
Verify DNS Settings
Ensure that DNS is configured correctly, and the server points to itself for DNS resolution. Launch the DNS Manager.

As you can see the forward lookup zone has been created for us us. It also created an A Record for me

But, the Reverse lookup Zone was not created. Right click to create a New Zone

Click Next to create a new reverse lookup Zone

I am fine with the default options.
This will create a copy of this zone that can be updated on this server.
This option will replicate to all DNS servers running in this domain

I will select the IPv4 option.

Enter your Network ID and click Next

This means, when devices are added to AD, records will be created automatically. Click Next.

Click Finish to complete this process.

Now, we have our reverse lookup zone created.

Let’s fix the Pinter Record for LabDC01. Update Pointer Record for Server. Right click on the record ad select properties.

Click the checkbox to select “update associated pointer (PRT) record

The associated pointer (PRT) record has been updated.

2. Manage Active Directory– Create OU and AD User Account
Open ‘Active Directory Users and Computers’ to manage users, groups, and organisational units. But in this guide, I will focus on creating AD User Account, and Organisation Unit

Click on Organisational Unit to create an OU.

Enter the OU name and click OK

to create a User, select the OU where you want the user to be. You can move the user around later on. Right click on the OU and select New, and then user.

Populate the New Object field for the user

Enter the password and select any applicable option for you and click Next.

Click Finish to complete this process

Our User has been created.

Conclusion on how to Setup a Domain Controller as Recommended by Microsoft
In this comprehensive guide, we have learnt how to install ADDS role onto Windows Sever, and promoted the Server as a domain controller. ALso, we created Organisational Units, and users. We also created a reverse look up zone for DNS and updated the PRT recorded for our Domain controller.
I hope you found this article on how to setup a Domain Controller as Recommended by Microsoft very useful. Please feel free to leave a comment below.